Understanding Apical Pneumothorax Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide

In the realm of pulmonary health, the diagnosis and treatment of a condition known as apical pneumothorax have garnered significant attention. Apical pneumothorax occurs when air accumulates in the pleural space at the apex, or the top, of the lung. This article aims to delve deep into the causes, symptoms, and most importantly, the effective apical pneumothorax treatment strategies available today. As the medical field advances, understanding the necessity of prompt and precise treatment methodologies becomes pivotal for healthcare providers and patients alike.
What is Apical Pneumothorax?
Apical pneumothorax is a subtype of pneumothorax characterized by the presence of air in the pleural cavity, predominantly affecting the apex of the lung. This condition can be classified into different categories:
- Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Occurs without any obvious cause, often seen in tall, young males.
- Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Develops in individuals with existing lung disease, such as COPD or cystic fibrosis.
- Traumatic Pneumothorax: Results from a physical injury to the chest wall.
Causes of Apical Pneumothorax
The development of apical pneumothorax can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Rupture of an Apical Bleb: Small air-filled sacs can form at the apex of the lungs, which may rupture spontaneously.
- Chest Trauma: Direct injuries such as fractures, stab wounds, or gunshot wounds can lead to air leakage.
- Underlying Lung Conditions: Diseases resulting in weakened lung tissue can predispose individuals to pneumothorax.
Symptoms of Apical Pneumothorax
Recognizing the symptoms of apical pneumothorax is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Sharp Chest Pain: Often unilateral and worsening with deep breaths.
- Dyspnea (difficulty breathing): Varies in severity depending on the extent of air in the pleural space.
- Decreased Breath Sounds: On clinical examination, physicians may note reduced breath sounds on auscultation.
Diagnostic Approach to Apical Pneumothorax
Upon presentation with potential symptoms, a thorough assessment is required to establish the diagnosis of apical pneumothorax. This typically includes:
- Clinical Evaluation: A detailed history and physical examination by a healthcare provider.
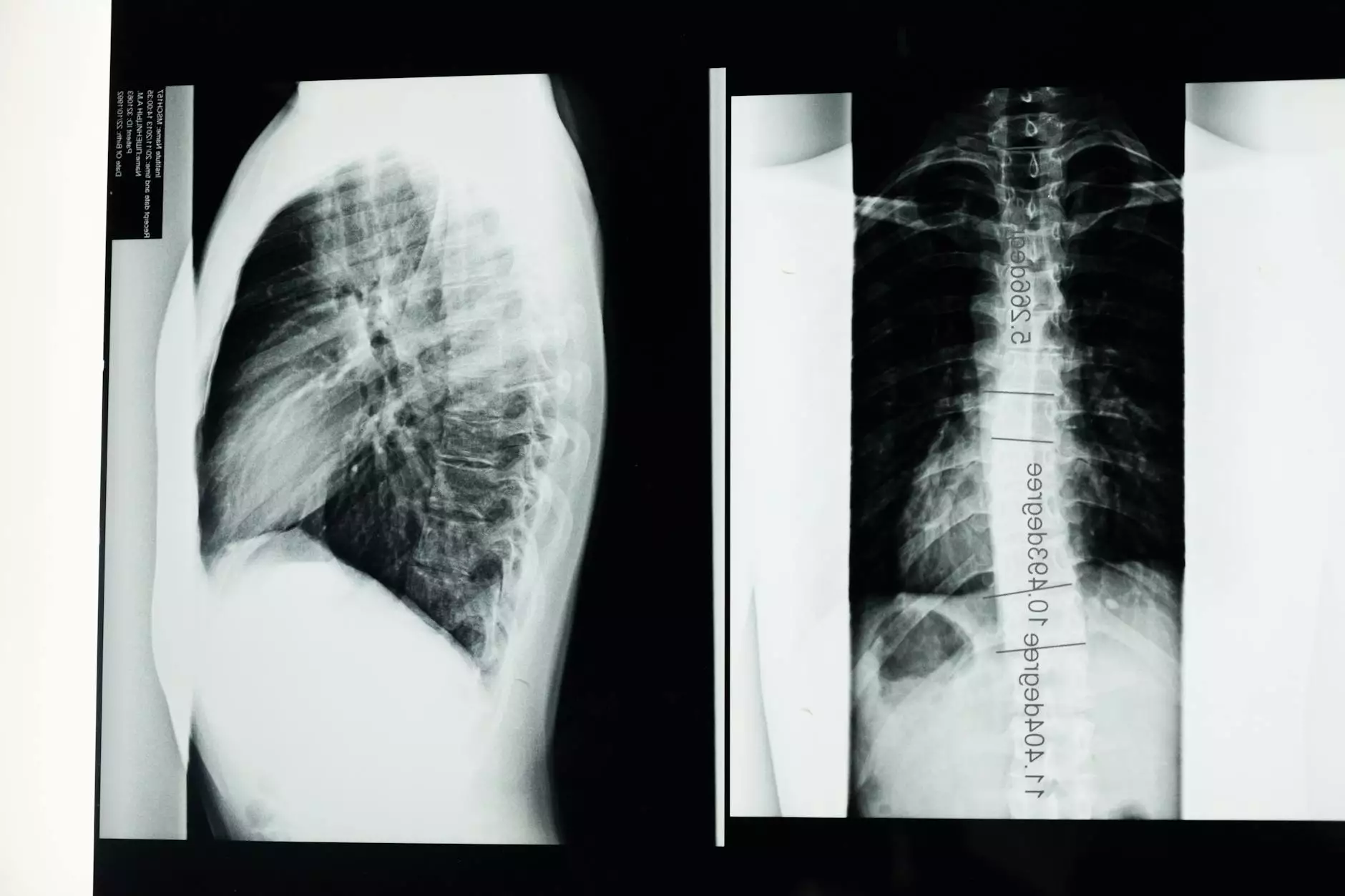
- Imaging Studies: Chest X-rays or CT scans are paramount for visualizing the presence of air in the pleural space.
- Ultrasound: An emerging modality that can aid in rapid assessment in emergency settings.
Apical Pneumothorax Treatment Options
Effective management of apical pneumothorax is crucial to avoid complications and promote optimal recovery. Treatment approaches may vary depending on the severity and cause of the condition.
1. Observation
In cases of small, asymptomatic apical pneumothorax, a strategy of careful observation may be adopted. This involves:
- Regular follow-ups to monitor size and symptoms.
- Educating patients about warning signs that necessitate immediate medical attention.
2. Needle Aspiration
For patients exhibiting moderate symptoms, needle aspiration serves as an effective treatment. This minimally invasive procedure entails:
- Inserting a needle into the pleural cavity to remove excess air.
- Providing immediate relief from symptoms.
3. Chest Tube Placement
In cases where the pneumothorax is large or symptomatic, chest tube placement is often warranted. This procedure involves:
- Inserting a tube into the pleural space to continuously remove air.
- Allowing the lung to re-expand as air is evacuated.
4. Surgical Intervention
When conservative measures fail, or in cases of recurrent pneumothorax, surgical options may be necessary. These include:
- Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): A minimally invasive approach to repair underlying blebs or defects.
- Thoracotomy: Open surgery may be required for extensive procedures or complicated cases.
Post-Treatment Care and Follow-Up
After the initiation of treatment for apical pneumothorax, post-care strategies play a critical role in recovery:
- Pain Management: Ensuring adequate control of discomfort through prescribed medications.
- Respiratory Therapy: Encouraging deep breathing exercises to enhance lung expansion.
- Regular Follow-Ups: Monitoring for any recurrent symptoms or complications.
Prevention Strategies for Apical Pneumothorax
While it may not be possible to prevent all instances of apical pneumothorax, certain measures can significantly reduce risk:
- Avoiding High-Altitude Activities: Individuals prone to spontaneous pneumothorax should be cautious with activities that involve rapid changes in pressure.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking can improve overall lung health and reduce the incidence of pneumothorax.
- Treating Underlying Lung Conditions: Managing chronic pulmonary diseases effectively can lower the risk.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Apical Pneumothorax Management
Doctors, particularly specialists such as pulmonologists and thoracic surgeons, are integral in diagnosing and treating apical pneumothorax. Their expertise in assessing lung conditions ensures that patients receive the most appropriate and effective treatment. At Neumark Surgery, our team of healthcare professionals is committed to providing comprehensive care to individuals with various pulmonary conditions, including apical pneumothorax.
Conclusion
In summary, apical pneumothorax treatment is a multifaceted approach that necessitates skilled evaluation, timely intervention, and ongoing management strategies. Understanding this condition empowers both patients and providers to act swiftly and appropriately. If you experience symptoms associated with pneumothorax, seeking immediate medical care is crucial. For expert guidance on pulmonary health, feel free to consult the specialists at Neumark Surgery.
With the right knowledge and treatment approach, the outlook for individuals affected by apical pneumothorax can be remarkably positive.
apical pneumothorax treatment